Unique Info About Is 220 Single Phase Or 3

Understanding Electrical Phases
1. Single Phase vs. Three Phase — A Simple Breakdown
Okay, so you're wrestling with the question: "Is 220 single phase or 3 phase?" It's a fair question, and truthfully, it's a bit like asking if a car is a sedan or a truck based only on its color. The voltage (220 in this case) doesn't inherently tell you the number of phases. Think of phases as the different lanes of a highway bringing power to your devices. More lanes (phases) generally mean more power can be delivered efficiently.
In simple terms, single-phase power is what you typically find in your home. It's like having one lane of that electrical highway. Three-phase power, on the other hand, is more common in industrial and commercial settings where larger equipment needs a consistent and powerful electrical supply— imagine three lanes working together. Now, both single-phase and three-phase systems can operate at 220 volts. That's where the potential for confusion comes in!
The key is to look beyond just the voltage. Consider the application and the type of wiring involved. Is it powering your toaster, or a massive HVAC system? The answer to that question will likely point you in the right direction. Think of it like this: your toaster only needs a sip of energy, whereas the HVAC system is chugging down gallons of it!
We're going to unpack this a bit further to make it crystal clear. Hang tight, and we'll explore the telltale signs that distinguish single-phase 220V from its three-phase cousin. It's easier than you think, and we promise, no electrical engineering degree is required!

How To Wire A Single Phase 220 Outlet » Wiring Work
The 220 Volt Misconception
2. Delving Deeper
The common misconception is that 220 volts automatically equals something specific. But, alas, electricity is a bit more nuanced than that. It's like assuming everyone who wears glasses is a librarian. While there might be some overlap, the connection isn't absolute. Voltage just represents the electrical potential, the "push" behind the electrons. It doesn't tell you how those electrons are being delivered— single-file or in a synchronized swarm.
Think of voltage as the water pressure in a pipe. You can have high pressure (220 volts) in a single pipe (single phase) or high pressure spread across three separate, but interconnected, pipes (three phase). The "phase" refers to the number of alternating current (AC) waveforms that are delivered simultaneously. Single-phase has one, and three-phase has three, offset from each other.
So, how do you tell the difference? Look at the wiring. Single-phase 220V usually involves two wires (one hot, one neutral, and often a ground). Three-phase 220V will usually involve three "hot" wires, plus a neutral and ground in many configurations. This is a simplified explanation, and actual wiring configurations can vary, but it gives you a general idea. Also, consider the equipment being powered. High-power appliances, like welders, industrial motors, and some larger AC units, are very likely to be three-phase, where as your dryer or oven may use 220 single phase.
Don't worry if this sounds complicated. The good news is you don't necessarily need to become an electrician to figure this out. We'll provide some practical tips to help you identify which type of system you're dealing with.

How To Convert 3 Phase 440 Volts Into Single 220 Volt Electrical
Identifying Single Phase 220V
3. Spotting the Differences
In a typical residential setting, single-phase 220V is often used for appliances that require a substantial amount of power, but not as much as a full-blown industrial machine. Think about your electric clothes dryer, your electric oven, or your water heater. These appliances require more "oomph" than a standard 120V outlet can provide, but they don't need the sheer power of three-phase.
A key identifier is the plug configuration. 220V single-phase outlets typically have a distinct shape with either three or four prongs arranged in a way that prevents you from accidentally plugging in a 120V appliance. This is a safety feature, preventing damage to the appliance and potential electrical hazards. Check the appliance's nameplate, too. It should clearly state the voltage and phase requirements.
Another clue can be found at your electrical panel. Look for breakers that are double the width of a standard 120V breaker. These "double-pole" breakers supply 220V. In a single-phase system, this breaker will be feeding power to your 220V appliance. If you're unsure, it's always best to consult with a qualified electrician. Messing with electricity without proper knowledge is a recipe for disaster!
Ultimately, identifying single-phase 220V often involves a process of elimination. If it's in your house, it's powering a larger appliance, and the outlet looks different than your regular outlets, chances are good it's single-phase 220V. But when in doubt... call a pro!
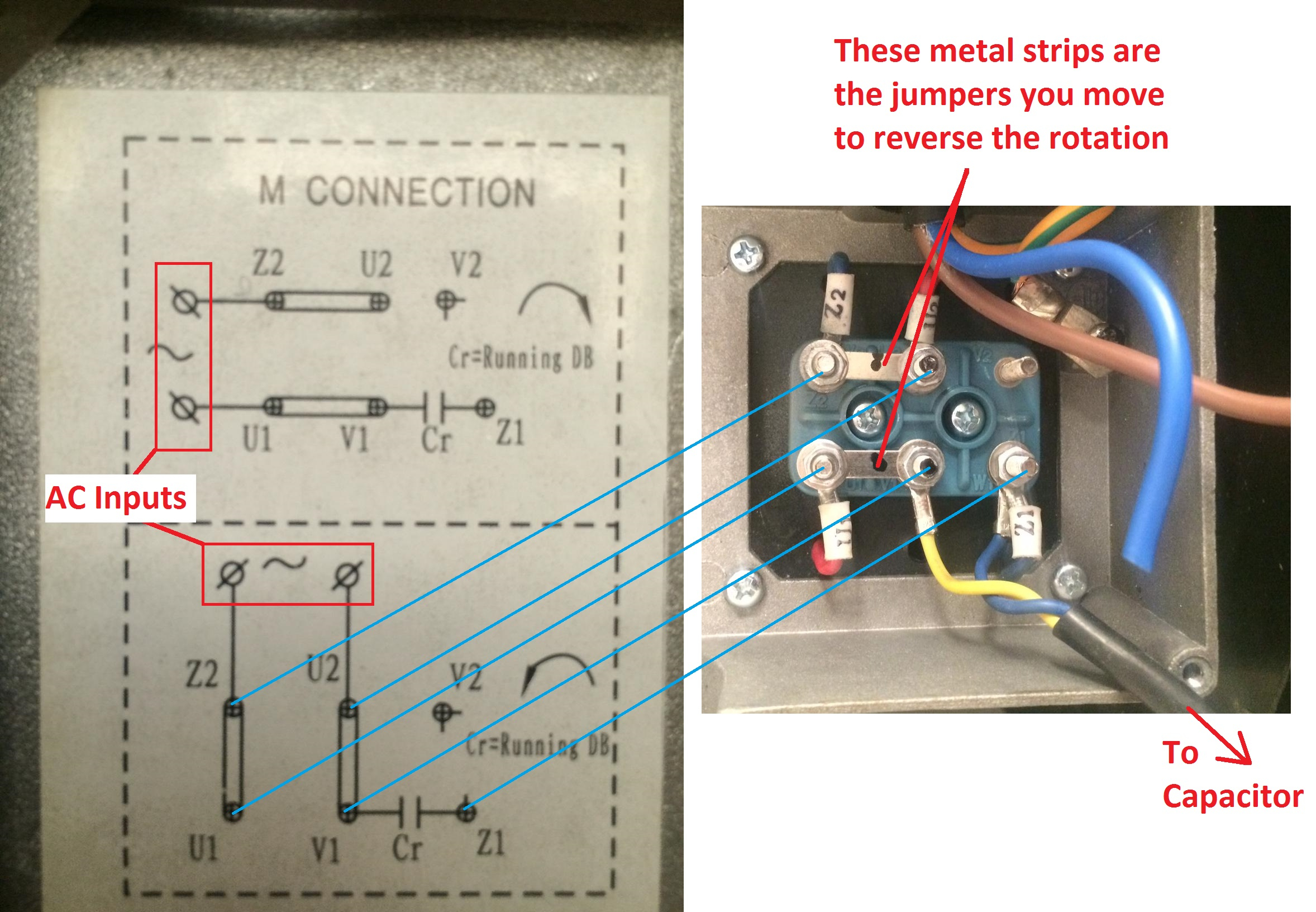
3 Phase 220 Volt Wiring Diagram
Recognizing Three Phase 220V
4. Unmasking Three Phase
Three-phase 220V is more commonly found in commercial and industrial settings where heavy machinery and equipment demand a consistently high power supply. Think factories, workshops, and large commercial buildings. These systems are designed to handle significantly larger electrical loads than single-phase systems can manage.
One of the most obvious indicators of three-phase power is the wiring configuration. As mentioned earlier, three-phase systems typically involve three "hot" wires, often accompanied by a neutral and a ground wire. This means the wiring and conduit will be significantly larger than what you'd find in a typical residential setup. The equipment powered by three-phase will also be substantially larger and more robust.
Another clue is the presence of a "delta" or "wye" configuration in the wiring. These are specific wiring arrangements used in three-phase systems to distribute power efficiently. Unless you're familiar with electrical diagrams, these configurations might look like gibberish, but they are dead giveaways that you're dealing with three-phase power. Consult an electrician if you're dealing with three phase power to avoid any injury.
Imagine trying to power a huge metal-stamping machine with a regular extension cord. It's just not going to happen! Three-phase power is the equivalent of a super-charged electrical system designed to handle these kinds of demanding applications. It's the backbone of many industries, enabling them to operate powerful equipment efficiently and reliably. So, unless you're running a factory in your garage, it's unlikely you have three-phase 220V at home.

Difference Between Singlephase And Threephase Power
FAQ
5. Frequently Asked Questions About Electrical Phases and Voltage
Let's tackle some common questions to solidify your understanding of electrical phases and voltage. Don't worry, we'll keep it simple and straightforward!
Q: Can I convert single-phase 220V to three-phase 220V?A: Technically, yes, but it's not as simple as flipping a switch. You'll need a rotary phase converter or a variable frequency drive (VFD). These devices essentially create a simulated third phase. However, it's often more cost-effective and reliable to have a dedicated three-phase power supply installed if you truly need it. Also, the "converted" three-phase power might not be suitable for all applications.
Q: Is three-phase power more dangerous than single-phase power?A: Both single-phase and three-phase power can be dangerous if not handled properly. The potential for electrical shock and fire is present in both systems. However, because three-phase systems typically involve higher voltages and currents, the potential for severe injury or damage is generally greater. Always exercise extreme caution and consult a qualified electrician when working with any electrical system.
Q: How can I tell for sure if my equipment needs single-phase or three-phase power?A: The best way is to check the equipment's nameplate or consult the manufacturer's specifications. The nameplate will clearly indicate the voltage, phase, and frequency requirements. Trying to power equipment with the wrong type of power can lead to damage, malfunction, or even fire.
Q: My neighbor told me 220V is always for heavy duty uses only. Is that true?A: Not quite. While 220V is used for higher power appliances, it's not strictly "heavy duty" in the industrial sense. Things like your clothes dryer or oven use 220V single-phase. True heavy duty, like factory equipment, will generally use three-phase power.
