Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About Is 0.8 Ohm Better Than 1.2
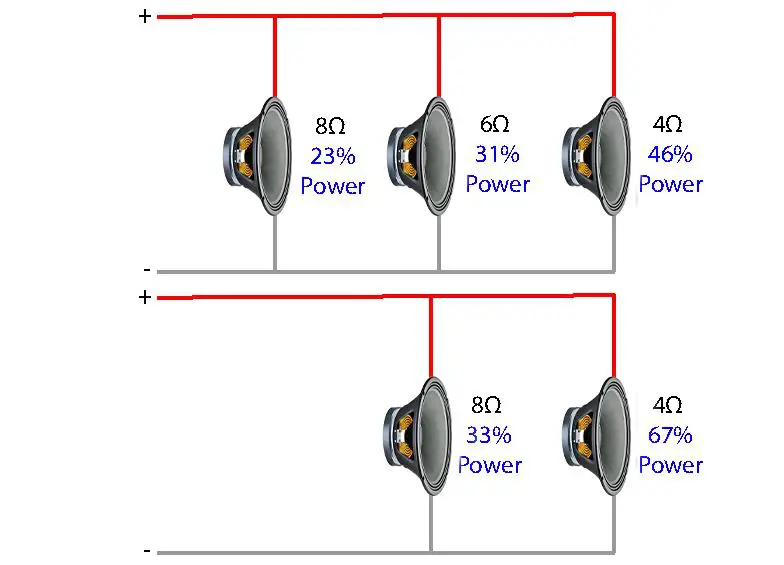
Are 4 Ohm Speakers Better Than 8 Speakers? BoomSpeaker
Ohm Sweet Ohm
1. Understanding Electrical Resistance
So, you're staring at two vaping coils, or maybe scrutinizing some audio equipment specs, and you see "0.8 ohm" and "1.2 ohm." Your brain probably chirps, "Numbers! Bigger? Smaller? What does it mean?!" Well, fear not, my friend! We're about to untangle this ohm-y mystery, and I promise, it's not as intimidating as it sounds. Think of ohms as a measure of electrical resistance. It's like a tiny bouncer at the door of your electrical circuit, dictating how easily current can flow through. A lower ohm value means less resistance, and a higher value means... you guessed it, more resistance.
It's easy to get bogged down in the technical stuff (and trust me, there's plenty!), but let's keep it simple. Imagine water flowing through a pipe. A narrow pipe (high resistance) restricts the water flow, while a wider pipe (low resistance) allows it to flow more freely. Electrical resistance works in a similar way, except instead of water, we're dealing with electrons doing the electric boogaloo. So, the big question isn't inherently whether 0.8 ohm or 1.2 ohm is "better," but rather, which one is more suitable for what you're trying to do.
The context is crucial. Are we talking about vaping coils? Speakers? Resistors in an electronic circuit? Each application has different requirements. For instance, in vaping, a lower resistance coil (like the 0.8 ohm) generally produces more vapor and a warmer vape because more current is drawn from the battery. In audio, impedance (which is related to resistance but not quite the same) affects how well your amplifier matches your speakers, and a mismatch can lead to poor performance or even damage.
So, remember, ohms aren't inherently good or bad; they're just a measure of resistance. What's "better" depends entirely on what you're plugging them into and what you're trying to achieve. We'll delve into specific scenarios shortly, but for now, just remember: lower ohms, less resistance, more current flow; higher ohms, more resistance, less current flow. Got it? Good! Now, let's move on to the fun stuff!
Vaping Adventures
2. The Vaporizer Verdict
Vaping! It's become a really huge topic now. The battle of the ohms is a very real thing. So, you're standing in a vape shop, staring at a wall of coils, and the shop assistant asks, "0.8 ohm or 1.2 ohm?" Panic sets in. Don't worry; I've been there. Here's the lowdown:
A 0.8 ohm coil, generally speaking, falls into the sub-ohm category. This means it's designed for direct-to-lung (DTL) vaping, where you inhale the vapor directly into your lungs like taking a breath. Sub-ohm coils produce more vapor, a warmer vape, and often enhanced flavor. They also require more power from your device and tend to use e-liquid more quickly. Think of it like a gas-guzzling sports car — powerful and fun, but thirsty.
On the other hand, a 1.2 ohm coil is typically a higher-resistance coil, often used for mouth-to-lung (MTL) vaping. This style mimics the sensation of smoking a cigarette, where you draw the vapor into your mouth first and then inhale. Higher-resistance coils produce less vapor, a cooler vape, and are more economical with e-liquid. They also require less power, making them ideal for smaller devices and longer battery life. Think of it like a fuel-efficient sedan — reliable, economical, and gets the job done without all the fuss.
So, which is "better"? It depends entirely on your vaping style and preferences. Do you crave massive clouds and intense flavor? Go for the 0.8 ohm. Prefer a more discreet vape with longer battery life? The 1.2 ohm might be your winner. Consider also the nicotine strength of your e-liquid. Sub-ohm vaping with high nicotine can be harsh, so lower nicotine levels are generally recommended.

Audio Authority
3. Sounds Good to Me?
Okay, let's switch gears from vaping to the world of audio. Here, we're not talking about ohms in the same way as resistance in a simple circuit, but rather about impedance, which is the AC equivalent of resistance. It's a measure of how much a speaker resists the flow of alternating current from an amplifier. Matching the impedance of your speakers to your amplifier is crucial for optimal sound quality and preventing damage to your equipment. Too much or too little impedance can both be problematic.
Why is impedance important? Think of it like this: your amplifier is trying to "push" electrical power into your speakers. If the speaker impedance is too low (say, 4 ohms when the amplifier is designed for 8 ohms), the amplifier has to work much harder to deliver the power, potentially leading to overheating and distortion. It's like trying to force too much water through a narrow pipe — something's gotta give.
Conversely, if the speaker impedance is too high (say, 16 ohms when the amplifier is designed for 8 ohms), the amplifier won't be able to deliver enough power to the speakers, resulting in weak sound and a loss of dynamic range. It's like trying to whisper across a football field — nobody's going to hear you.
So, in the audio world, the "better" impedance depends on the specifications of your amplifier and speakers. It's not about lower or higher being inherently better, but about finding the right match to ensure optimal performance and protect your equipment. Consult your amplifier and speaker manuals to determine the recommended impedance range. Mismatched impedance can be a real bummer.

Perhatikan Gambar Di Rangkaian Listrik Berikut Jika R1 = 4 Ohm R2 2
Electronics Engineering
4. Resistance is NOT Futile (Usually)
Now, let's venture into the world of electronics. Here, resistors are essential components that control the flow of current in a circuit. They come in various values, measured in ohms, and are used for a multitude of purposes, such as limiting current, dividing voltage, and providing bias for transistors.
In this context, whether a 0.8 ohm resistor is "better" than a 1.2 ohm resistor depends entirely on the specific application. If you need to limit current to a certain level, you'll choose a resistor value that achieves that goal. A lower resistance will allow more current to flow, while a higher resistance will restrict it.
For example, if you're trying to light an LED, you'll need a resistor to limit the current flowing through it. Without a resistor, the LED would draw too much current and burn out. The appropriate resistor value will depend on the LED's voltage and current requirements, as well as the voltage of the power supply. Calculating the correct resistor value is crucial for ensuring the LED operates safely and reliably.
Therefore, in electronics, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. The "better" resistor is the one that fulfills the specific requirements of the circuit. Understanding Ohm's Law (Voltage = Current x Resistance) is fundamental to choosing the correct resistor values for any electronic application.

Making the Right Choice
5. Putting It All Together
So, we've explored ohms in various contexts, from vaping to audio to electronics. Hopefully, you're starting to see that the question of "better" is highly dependent on the specific application. But let's recap some key considerations to help you make the right choice:
Application: What are you using the component for? Vaping, audio, or electronics will influence the required impedance or resistance.
Device Specifications: Check the specifications of your devices. What resistance range is best for this usage?
Personal Preference: This is very subjective. Do you want more or less vapor?In the end, understanding the basic principles of resistance and impedance will empower you to make informed decisions and choose the components that best suit your needs. Don't be afraid to experiment and learn — that's how the electrical magic happens!

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Ohm-azing Answers!
Still scratching your head? Here are some frequently asked questions to further clarify the ohm-y world:
Q: What happens if I use a speaker with the wrong impedance?
A: Using a speaker with an impedance that's too low can overload your amplifier, potentially causing it to overheat and distort the sound. Using a speaker with an impedance that's too high can result in weak sound and a loss of dynamic range.
Q: Can I use a lower resistance coil on my vape if my device is designed for higher resistance?
A: It's generally not recommended. Lower resistance coils require more power, and if your device isn't designed to deliver that power, it could overheat, damage the battery, or not work at all.
Q: Does a lower ohm resistor always mean more current?
A: Yes, for a given voltage, a lower resistance will always result in more current flow, according to Ohm's Law (I = V/R).
Q: Why all the hype about Ohm's law?
A: Ohms Law is useful for calculating voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. By understanding and using this law, engineers can design circuits for a number of purposes.